Understanding Prefabricated Homes: Affordable and Efficient Housing Options
Prefabricated homes are residential units manufactured in controlled facilities and assembled on-site. This approach integrates standardized components, quality control, and streamlined logistics to reduce on-site labor and construction time. The article explains how prefab housing functions and key considerations.
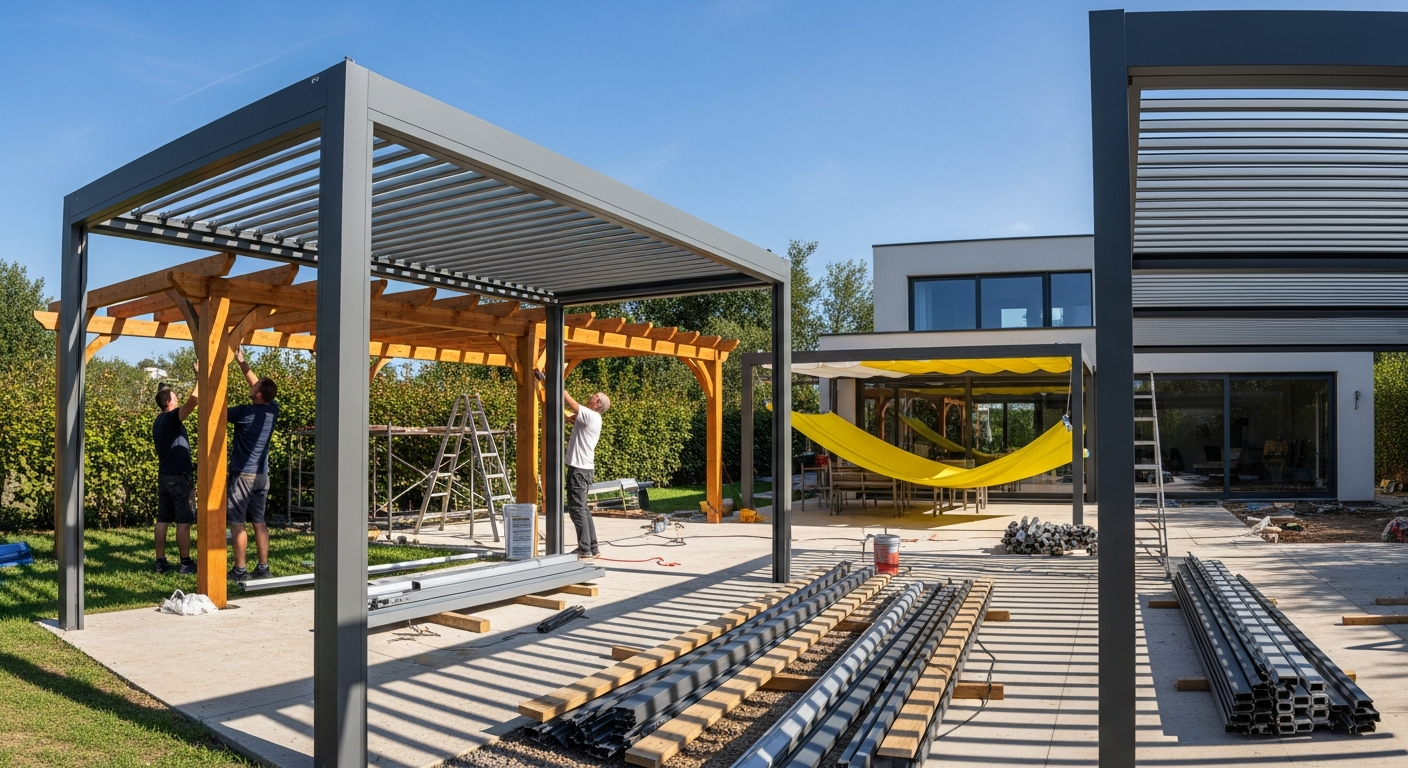

Prefabricated housing represents a shift in how residential structures are conceived, manufactured, and assembled. Unlike traditional homes built entirely on-site, prefab homes are constructed in controlled factory environments before being transported and assembled at their final locations. This manufacturing approach reduces weather-related delays, minimizes material waste, and allows for precise quality control throughout the building process. The concept has evolved significantly from its mid-century origins, now encompassing sophisticated architectural designs that rival custom-built homes in both aesthetics and functionality.
What are prefabricated homes and how do they work?
Prefabricated homes are residential structures where major components or entire sections are manufactured in a factory setting before being transported to the building site for assembly. The process typically begins with design selection and site preparation while factory production occurs simultaneously. Manufacturers construct walls, floors, roof systems, and even install plumbing and electrical components in climate-controlled facilities. Once completed, these modules or panels are shipped to the property, where they are assembled on a prepared foundation. The entire process, from order to move-in, often takes three to six months compared to the eight to twelve months typical for conventional construction. This efficiency stems from parallel workflows, standardized processes, and elimination of weather-related interruptions that commonly delay traditional builds.
How do efficient prefabricated homes compare to traditional construction?
The efficiency advantages of prefabricated construction extend beyond simple time savings. Factory-built homes generate approximately 50 percent less construction waste than site-built homes due to precise material calculations and the ability to recycle excess materials within the manufacturing facility. Energy efficiency often surpasses traditional construction because factory settings allow for tighter building envelopes, better insulation installation, and more consistent quality control. Many prefab manufacturers incorporate energy-efficient windows, enhanced insulation packages, and modern HVAC systems as standard features. Labor efficiency also improves significantly since skilled workers operate in controlled environments with optimized workflows rather than adapting to varying site conditions. However, traditional construction offers greater flexibility for mid-project design changes and may be preferable for complex custom designs or challenging building sites with difficult access.
What types of prefabricated home designs are available?
The prefabricated housing market encompasses several distinct categories, each with unique characteristics. Modular homes consist of multiple three-dimensional sections built in factories and assembled on-site, offering the widest range of customization and often appearing indistinguishable from traditional homes. Panelized homes arrive as flat wall, floor, and roof panels that are assembled on-site, providing flexibility while maintaining factory precision. Manufactured homes, previously called mobile homes, are built entirely in factories on permanent steel chassis and transported as complete units. Tiny homes represent a growing segment, typically under 400 square feet, emphasizing minimalism and mobility. Contemporary designs now include multi-story configurations, modern architectural styles with clean lines and large windows, traditional aesthetics mimicking craftsman or farmhouse styles, and sustainable designs incorporating green building principles. Many manufacturers offer semi-custom options where buyers select from base models and modify floor plans, finishes, and features within structural parameters.
Understanding prefabricated home costs and providers
Prefabricated home pricing varies considerably based on size, design complexity, materials, and regional factors. Understanding these costs helps prospective buyers budget appropriately and compare options effectively. Base prices for prefab homes typically range from 100 to 200 dollars per square foot for the manufactured components, though luxury models can exceed 300 dollars per square foot. These figures generally exclude site preparation, foundation work, utility connections, transportation, and assembly costs, which can add 25 to 50 percent to the total project expense. A modest 1,200 square foot modular home might cost between 120,000 and 240,000 dollars for the home itself, with total project costs reaching 180,000 to 360,000 dollars after site work and installation.
| Provider Type | Services Offered | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| National Modular Builders | Complete home packages, customization, delivery | 150,000 - 400,000 dollars for turnkey projects |
| Regional Manufacturers | Standard models, limited customization, local delivery | 100,000 - 250,000 dollars including installation |
| Luxury Prefab Companies | Architect-designed homes, premium materials, full customization | 300,000 - 800,000 dollars or more |
| Kit Home Providers | DIY assembly packages, basic designs, owner coordination | 50,000 - 150,000 dollars for materials only |
| Container Home Specialists | Converted shipping containers, modern industrial designs | 80,000 - 200,000 dollars completed |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Financing prefabricated homes can present challenges since some lenders treat them differently than traditional construction. However, many modular homes qualify for conventional mortgages once permanently affixed to land and foundations, while manufactured homes may require specialized financing with different terms. Prospective buyers should consult with lenders experienced in prefab financing early in the planning process.
How do zoning laws and building codes affect prefab installation and global uses?
Navigating regulatory requirements represents a critical aspect of prefabricated home installation. In the United States, modular and panelized homes must meet the same International Residential Code standards as site-built homes, inspected by local building officials during and after installation. Manufactured homes follow the federal HUD Code, which differs from local building codes and may face restrictions in certain zoning districts. Local zoning ordinances determine where prefab homes can be placed, with some municipalities maintaining minimum square footage requirements, architectural standards, or outright prohibitions on certain prefab types in specific neighborhoods. Prospective buyers should verify zoning compliance and obtain necessary permits before purchasing. Foundation requirements, setback distances, utility connection standards, and aesthetic guidelines all vary by jurisdiction. Some progressive communities actively encourage prefab construction through streamlined approval processes, recognizing these homes as solutions to housing affordability challenges. Internationally, prefabricated housing has gained significant traction in countries facing housing shortages or seeking sustainable building methods. Scandinavian countries have embraced factory-built homes for decades, while Japan leads in earthquake-resistant prefab technology. Developing nations increasingly adopt prefab solutions for rapid housing deployment in growing urban areas.
Making informed decisions about prefabricated housing
Choosing a prefabricated home requires careful evaluation of personal needs, site characteristics, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Successful projects begin with thorough research into reputable manufacturers, clear understanding of total costs beyond base prices, and realistic timelines accounting for site preparation and local approval processes. Site accessibility for delivery trucks, foundation requirements for soil conditions, utility availability, and neighborhood compatibility all influence project feasibility. Working with experienced contractors familiar with prefab installation, consulting with local building departments early, and visiting completed projects or factory facilities helps buyers make confident decisions. While prefabricated homes offer compelling advantages in cost predictability, construction speed, and quality consistency, they represent significant investments requiring the same due diligence as traditional home purchases. Understanding the complete process, realistic cost expectations, and regulatory landscape empowers buyers to determine whether prefabricated construction aligns with their housing needs and financial circumstances.