Prefabricated Homes – Affordable and Efficient Housing Options with Fast Installation
Prefabricated homes represent a revolutionary approach to residential construction, offering homeowners a faster, more cost-effective alternative to traditional building methods. These factory-built structures combine quality craftsmanship with streamlined production processes, delivering complete housing solutions that can be assembled on-site in a fraction of the time required for conventional construction.
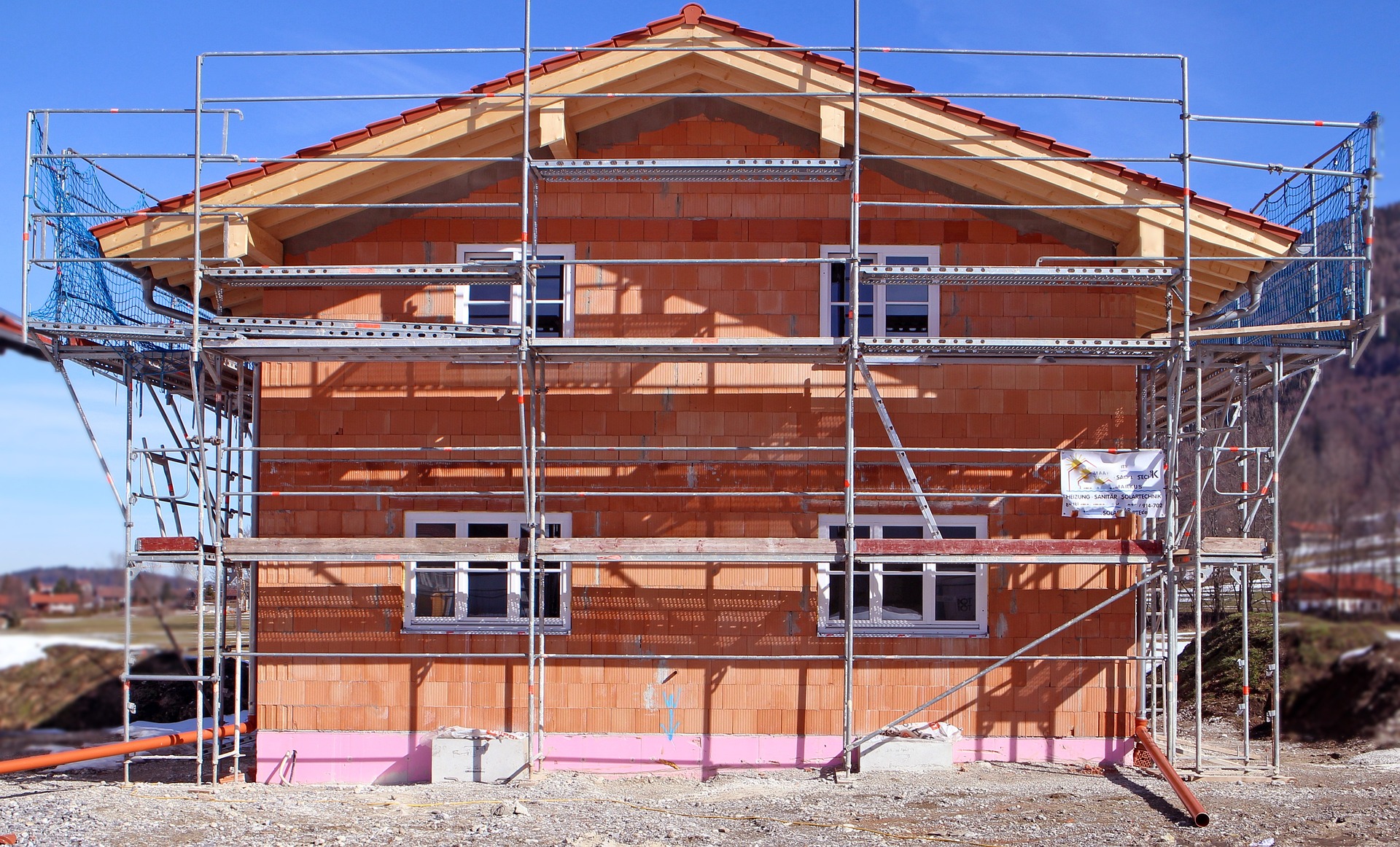

Prefabricated homes represent a growing segment of the Australian housing market, offering practical solutions for those seeking quality accommodation without the extended timelines and unpredictability associated with traditional construction. As building costs continue to rise and housing demand increases, understanding the mechanics, benefits, and considerations of prefab housing becomes essential for informed decision-making.
What Are Prefabricated Homes and How Do They Work?
Prefabricated homes are residential structures manufactured in controlled factory environments before being transported to their final location for assembly. The construction process involves building major components or entire modules indoors, where weather delays and material theft are eliminated. Once manufacturing is complete, these sections are transported to the building site and assembled on a prepared foundation, typically within days or weeks rather than months. The factory setting allows for precise quality control, standardized building practices, and efficient use of materials. Australian prefab manufacturers utilize advanced construction techniques, including computer-aided design and precision cutting equipment, ensuring consistent quality across all units. The process typically involves site preparation, foundation work, delivery of prefabricated sections, assembly, and connection of utilities, with total project timelines often reduced by 30 to 50 percent compared to traditional builds.
How Do Efficient Prefabricated Homes Compare to Traditional Construction?
When comparing prefabricated homes to traditional construction methods, several distinct differences emerge across cost, timeline, quality, and environmental impact. Traditional construction involves on-site building from foundation to roof, with materials delivered as needed and work progressing sequentially through various trades. This method typically takes six to twelve months for completion and faces frequent delays due to weather, material availability, and coordination challenges. Prefabricated construction, by contrast, allows simultaneous site preparation and factory building, reducing overall project duration significantly. Quality control benefits from the factory environment, where inspections occur at multiple stages under consistent conditions. Material waste is typically reduced by 20 to 30 percent in prefab construction due to precise measurements and efficient material use. Energy efficiency often surpasses traditional builds because of tighter construction tolerances and modern insulation techniques applied in controlled settings. However, traditional construction offers greater customization flexibility and may be preferred for complex architectural designs or challenging sites where transportation of large modules proves difficult.
What Types of Prefabricated Home Designs Are Available?
The Australian prefab market offers diverse design options catering to various lifestyle needs, budgets, and aesthetic preferences. Modular homes consist of multiple factory-built sections assembled on-site, ranging from compact one-bedroom units to expansive family homes with multiple levels. Panelized systems involve flat-packed wall, floor, and roof panels assembled on-site, offering flexibility in design while maintaining factory-built quality. Kit homes provide pre-cut materials and components for owner-builders or local contractors to assemble, representing the most affordable prefab option. Shipping container homes repurpose industrial containers into modern dwellings, appealing to those seeking sustainable and unique architectural solutions. Tiny homes, typically under 50 square meters, address minimalist living trends and affordability concerns. Design styles span from contemporary minimalist aesthetics with clean lines and open-plan layouts to traditional Australian designs featuring verandas and pitched roofs. Many manufacturers offer customization options including floor plan modifications, material selections, fixture choices, and energy-efficient upgrades such as solar panels and rainwater collection systems.
How Do Zoning Laws and Building Codes Affect Prefab Installation?
Navigating regulatory requirements represents a critical aspect of prefab home installation in Australia. All prefabricated homes must comply with the National Construction Code and relevant Australian Standards, regardless of their manufacturing method. Local council regulations govern land use, setbacks, height restrictions, and design guidelines that vary significantly between jurisdictions. Before purchasing a prefab home, buyers must verify that their chosen model meets local planning requirements and obtain necessary development approvals. Some councils maintain specific provisions for relocatable or modular homes, while others treat them identically to traditional construction. Zoning classifications determine permitted land uses, with residential zones typically accommodating prefab homes without issue, though rural or industrial zones may require special consideration. Building permits are mandatory, requiring submission of engineering plans, energy efficiency reports, and compliance documentation. Site-specific considerations include bushfire attack level ratings in fire-prone areas, flood planning levels in flood zones, and soil classification reports affecting foundation design. Engaging with council planning departments early in the process helps identify potential obstacles and ensures smooth approval processes. Some manufacturers provide assistance with regulatory compliance, while others expect buyers to manage approvals independently.
Cost Considerations and Pricing Insights
Understanding the financial aspects of prefabricated homes helps potential buyers make informed decisions. Base prices for prefab homes in Australia typically range from 1,500 to 3,500 dollars per square meter, depending on design complexity, materials, and included features. A basic modular home of 100 square meters might cost between 150,000 and 250,000 dollars for the structure alone, while luxury designs with premium finishes can exceed 400,000 dollars. These figures generally exclude site preparation, foundation work, utility connections, and transportation costs, which can add 50,000 to 100,000 dollars or more to the total project cost. Kit homes represent the most economical option, with basic models starting around 80,000 dollars for smaller designs, though buyers must factor in construction labor if not undertaking the build themselves. Shipping container homes typically range from 100,000 to 300,000 dollars depending on size and fit-out level. When comparing costs to traditional construction, prefab homes often deliver savings of 10 to 30 percent, though final costs depend heavily on site conditions, location, and customization choices.
| Home Type | Typical Size Range | Estimated Cost Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modular Home | 80-200 sqm | 150,000-400,000 AUD | Includes factory build, excludes site costs |
| Kit Home | 60-150 sqm | 80,000-200,000 AUD | Requires assembly labor, materials included |
| Panelized System | 100-180 sqm | 180,000-350,000 AUD | Mid-range customization, faster than traditional |
| Container Home | 40-120 sqm | 100,000-300,000 AUD | Unique design, sustainability focus |
| Tiny Home | 20-50 sqm | 60,000-150,000 AUD | Minimal footprint, lower ongoing costs |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
What Unique Benefits Do Prefabricated Homes Offer Worldwide?
Prefabricated housing delivers advantages that extend beyond Australian borders, addressing global housing challenges through innovation and efficiency. Speed of construction ranks among the most significant benefits, with some projects completed in weeks rather than months, providing rapid housing solutions for disaster relief, population growth, and urgent accommodation needs. Environmental sustainability improves through reduced material waste, lower transportation emissions from consolidated deliveries, and enhanced energy efficiency from precision construction methods. Quality consistency results from factory conditions where skilled workers use standardized processes and materials are protected from weather exposure. Cost predictability increases as factory production minimizes unexpected expenses and delays common in traditional construction. Labor efficiency addresses skilled worker shortages by concentrating construction in controlled environments where productivity increases and training becomes more effective. Flexibility allows manufacturers to adapt designs for various climates, cultural preferences, and regulatory environments, making prefab solutions viable across diverse global markets. Scalability enables rapid production increases to meet housing demands following natural disasters or during periods of population growth. As technology advances and acceptance grows, prefabricated homes continue evolving, incorporating smart home features, renewable energy systems, and innovative materials that push the boundaries of residential construction worldwide.
Conclusion
Prefabricated homes offer Australians a compelling alternative to traditional construction, combining affordability, efficiency, and quality in a streamlined building process. From understanding how these homes are manufactured and assembled to navigating regulatory requirements and comparing costs, informed buyers can leverage the benefits of prefab construction to achieve their housing goals. As the industry continues to mature and innovate, prefabricated housing stands positioned to play an increasingly important role in addressing Australia’s housing needs while offering diverse design options that suit various lifestyles and budgets.