Industrial Machines: Backbone of Modern Manufacturing
Manufacturing has evolved dramatically over the past century, transforming from labor-intensive processes to sophisticated automated systems. At the heart of this transformation lie industrial machines - complex mechanical systems that have revolutionized how products are designed, produced, and delivered to consumers worldwide.
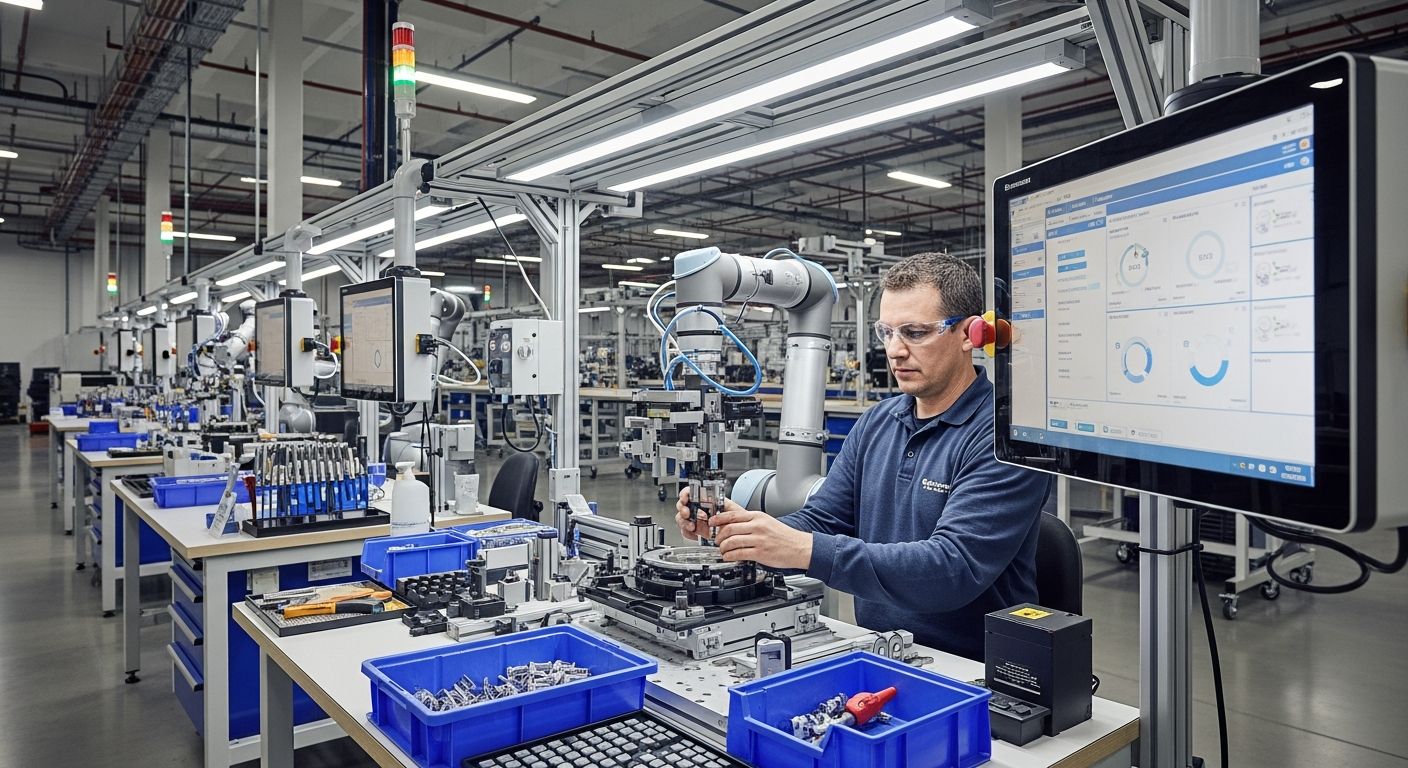

The manufacturing sector relies heavily on sophisticated equipment designed to perform specific tasks with precision and consistency. Advanced machinery encompasses a broad range of devices, from heavy-duty presses and lathes to computerized robotic systems and conveyor networks. These tools form the core infrastructure of production facilities across numerous industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
Modern manufacturing environments integrate multiple machine types to create efficient production workflows. Each piece of equipment plays a distinct role in transforming raw materials into finished products, with coordination between systems ensuring smooth operations and minimal downtime.
How Modern Machinery Drives Efficiency in Manufacturing
Efficiency in manufacturing depends on the ability to produce high volumes of consistent quality products within reasonable timeframes. Advanced machinery achieves this through automation, precision engineering, and continuous operation capabilities. Automated systems reduce human error and increase production speed, allowing facilities to operate around the clock with minimal supervision.
Computer numerical control technology enables equipment to execute complex operations with micrometer-level accuracy, ensuring each component meets exact specifications. This precision reduces material waste and minimizes the need for quality control interventions. Additionally, modern equipment incorporates sensors and monitoring systems that detect anomalies in real time, preventing defects before they occur.
Integrated manufacturing systems connect multiple devices through centralized control platforms, optimizing workflow and resource allocation. This connectivity allows production managers to adjust parameters dynamically, responding to changing demands or material availability without halting operations.
The Role of Advanced Equipment in Shaping the Future of Production
Technological advancement continues to reshape manufacturing capabilities, with production equipment incorporating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things connectivity. These innovations enable predictive maintenance, where equipment monitors its own condition and schedules servicing before failures occur, reducing unexpected downtime.
Additive manufacturing technologies, commonly known as 3D printing, have expanded production possibilities by allowing complex geometries that traditional subtractive methods cannot achieve. Large-scale additive systems now produce functional components for aerospace, medical, and automotive applications, complementing conventional manufacturing processes.
Robotic systems have evolved beyond simple repetitive tasks to handle intricate assembly operations, quality inspection, and material handling. Collaborative robots work alongside human operators, combining machine precision with human problem-solving abilities. This partnership enhances productivity while maintaining workplace safety.
Sustainability concerns drive development of energy-efficient equipment that reduces environmental impact. Modern machinery incorporates power management systems, waste reduction features, and recyclable component designs, aligning manufacturing practices with environmental responsibility goals.
How Advanced Systems Improve Manufacturing Processes
Advanced machinery introduces capabilities that fundamentally improve production methodologies. Multi-axis machining centers perform multiple operations in a single setup, reducing handling time and improving dimensional accuracy. Laser cutting and welding systems provide clean, precise material processing with minimal thermal distortion.
Automated material handling systems transport components between workstations efficiently, reducing labor requirements and cycle times. Automated guided vehicles and conveyor networks move materials throughout facilities without human intervention, optimizing floor space utilization and workflow organization.
Quality assurance benefits significantly from machine vision systems that inspect products at production speeds impossible for human operators. These systems detect surface defects, dimensional variations, and assembly errors with consistent accuracy, ensuring only conforming products reach customers.
Data collection capabilities embedded in modern equipment provide valuable insights into production performance. Manufacturers analyze this information to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and forecast maintenance needs, creating continuous improvement cycles that enhance overall operational effectiveness.
Why Production Equipment Is Essential for Today’s Manufacturing Success
Competitiveness in global markets requires manufacturers to deliver quality products at competitive prices with reliable delivery schedules. Advanced production equipment provides the foundation for meeting these requirements through consistent output, scalability, and adaptability to changing market conditions.
Customization demands have increased as consumers seek personalized products. Flexible manufacturing systems equipped with programmable equipment accommodate product variations without extensive retooling, enabling mass customization strategies that were previously economically unfeasible.
Labor availability challenges in many regions make automation increasingly necessary. Automated systems fill workforce gaps while allowing human workers to focus on skilled tasks requiring judgment, creativity, and problem-solving abilities. This division of labor maximizes productivity and job satisfaction.
Quality standards continue rising across industries, with regulatory requirements demanding traceability and documentation. Production equipment with data logging and reporting capabilities automatically generates compliance records, simplifying regulatory adherence and reducing administrative burdens.
Supply chain resilience has become critical in recent years. Manufacturers with advanced machinery can quickly adjust production to accommodate material substitutions or design modifications, maintaining operations despite external disruptions.
| Equipment Category | Common Applications | Key Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining Centers | Precision component manufacturing | Multi-axis cutting, high accuracy |
| Robotic Systems | Assembly, welding, material handling | Programmable, repeatable motions |
| Injection Molding Equipment | Plastic component production | High-volume production, complex shapes |
| Laser Processing Systems | Cutting, welding, marking | Precision, minimal material waste |
| Automated Packaging Lines | Product packaging and labeling | High-speed operation, quality verification |
The landscape of manufacturing continues evolving as technological innovations emerge and market demands shift. Production equipment remains central to manufacturing success, providing the capabilities necessary to compete in dynamic global markets. Facilities that invest in modern systems position themselves to capitalize on opportunities while maintaining operational excellence.
Manufacturers must carefully evaluate their specific needs when selecting equipment, considering factors such as production volumes, product complexity, quality requirements, and future growth plans. Proper equipment selection, combined with skilled operators and effective maintenance programs, creates the foundation for sustainable manufacturing success in an increasingly competitive environment.