Dental Implants in Canada 2026 Overview
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots surgically placed into the jawbone to support replacement teeth. In Canada, they are used to restore function and appearance after tooth loss. This overview explains the implant process, typical costs, benefits, and care considerations relevant for 2026.
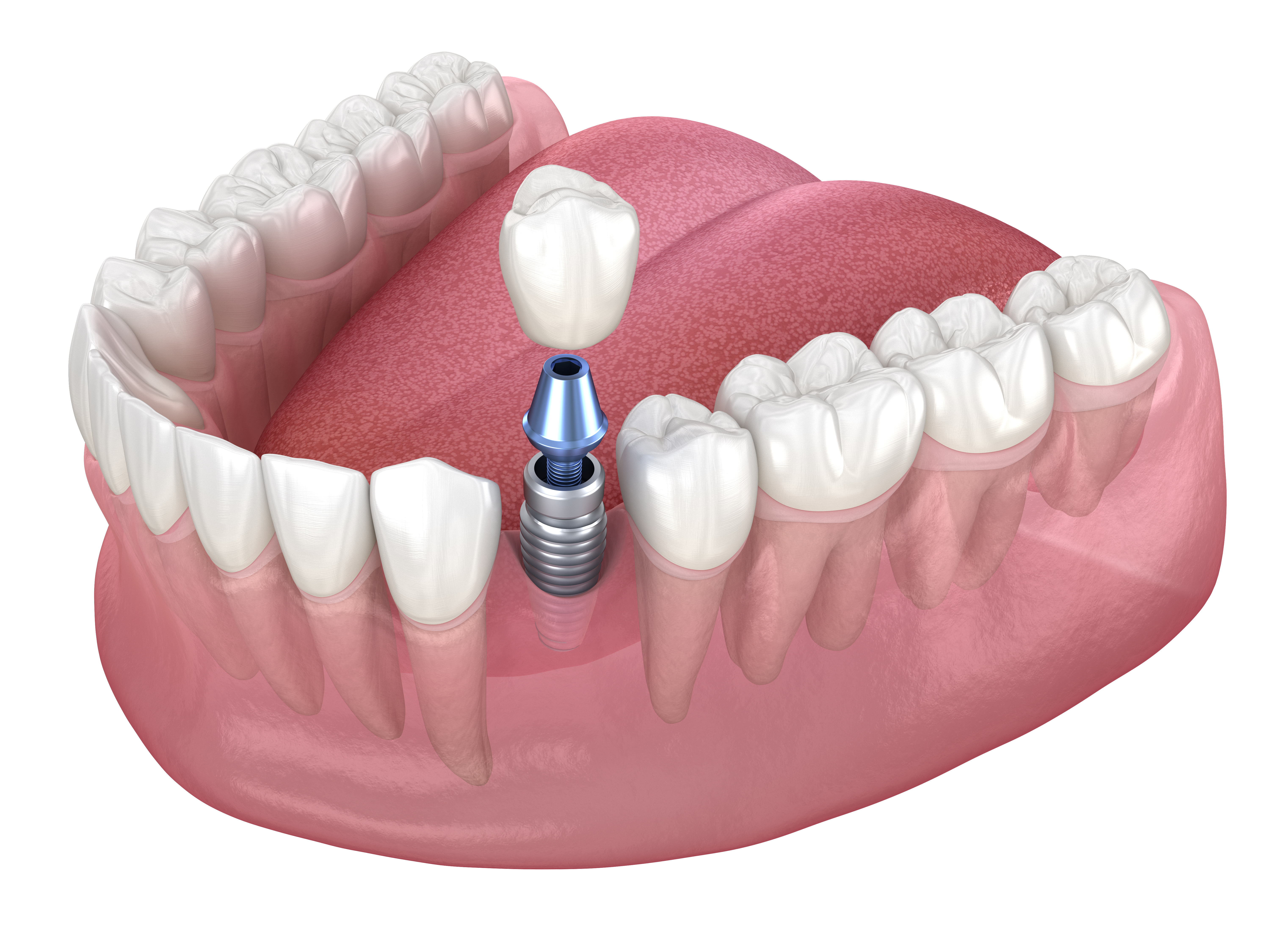
What Are Dental Implants?
Dental implants consist of small titanium posts inserted into the jawbone to replace the roots of missing teeth. Once placed, they bond with the bone through a process called osseointegration. This fusion provides a stable foundation to attach artificial teeth such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. Implants aim to mimic natural tooth function and appearance.
Unlike removable dentures or traditional bridges, implants integrate with the jawbone, which can help maintain bone density and prevent the bone loss commonly associated with missing teeth. This integration contributes to improved chewing ability and speech compared to some conventional prosthetics.
The Dental Implant Procedure
The implant process typically occurs in several stages over several months, allowing for adequate healing:
-
Initial Evaluation: A dentist or specialist assesses oral health, bone density, and suitability through clinical examination and imaging such as X-rays or CT scans.
-
Surgical Placement: The titanium implant is surgically inserted into the jawbone under local anesthesia. Depending on the case, this might be done by a general dentist, periodontist, or oral surgeon.
-
Osseointegration Period: After placement, the implant is left to integrate with the bone. This process generally takes 3 to 6 months, varying by individual health and bone quality.
-
Abutment Placement: Once integration is sufficient, an abutment (a connector) is attached to the implant. This part will support the artificial tooth.
-
Restoration: The final stage involves placing the crown, bridge, or denture on the abutment. Impressions are taken beforehand to ensure a proper fit and appearance.
Follow-up visits ensure the implant and restoration maintain stability and function over time.
Types of Dental Implants
Several options exist for dental implants depending on the clinical situation:
- Endosteal Implants: The most common type, placed directly into the jawbone.
- Subperiosteal Implants: Placed under the gum but on or above the jawbone, used when there is insufficient bone height.
- Zygomatic Implants: Less common, anchored in the cheekbone for cases with severe upper jaw bone loss.
Implant-supported restorations may replace a single tooth, multiple teeth, or provide support for full dentures.
Typical Costs in Canada (2026)
When considering dental implants in Canada, typical price ranges include: - Basic option: Around CAD $1,500 to $2,500 per implant - covers implant placement and healing but usually excludes the prosthetic tooth. - Standard option: Approximately CAD $3,000 to $5,000 per implant including the surgical placement and a single crown restoration. - Complex cases: Costs can increase beyond CAD $6,000 per implant if additional procedures, such as bone grafting or sinus lifts, are required.
Costs vary based on location, provider expertise, number of implants, and individual treatment needs. Some provincial health plans or private insurance may offer partial coverage; these vary significantly.
Advantages of Dental Implants
Dental implants offer several advantages over traditional tooth replacement options:
- Bone Preservation: By stimulating the jawbone, implants help maintain bone volume and facial structure.
- Stability and Function: Implants provide a secure base, allowing for natural chewing efficiency.
- Durability: With appropriate care, implants can last many years or decades.
- Improved Speech: Stable teeth reduce speech difficulties sometimes caused by loose dentures.
- No Impact on Adjacent Teeth: Unlike bridges, implants do not rely on neighboring teeth for support.
Potential Risks and Considerations
As with any surgical procedure, dental implants carry potential risks including:
- Infection at the Implant Site
- Injury or Damage to Surrounding Structures such as nerves or teeth
- Implant Failure possibly due to poor osseointegration or overloading
- Sinus Problems in upper jaw implants if they protrude into sinus cavities
Certain health conditions may affect the success of implants, including uncontrolled diabetes, smoking, osteoporosis, or immune disorders. A thorough medical and dental assessment is critical.
Aftercare and Maintenance
Maintaining implant health includes:
- Practicing good oral hygiene with regular brushing and flossing to prevent peri-implant disease.
- Attending routine dental check-ups for professional cleaning and monitoring.
- Avoiding habits that strain implants, such as smoking or chewing hard objects.
Proper care helps reduce complications and prolongs the lifespan of implants.
Healthcare Professionals Involved in Dental Implants
In Canada, dental implants may be placed by different types of professionals:
- General Dentists with training in implant dentistry
- Periodontists specializing in gum and bone care
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons trained in surgical placement
The restoration phase, attaching crowns or dentures to implants, is often managed by general dentists or prosthodontists.
Regulatory and Professional Standards
Dental implant procedures in Canada follow provincial regulations and standards established by dental regulatory authorities. Practitioners must maintain licensure and adhere to guidelines regarding patient assessment, informed consent, and treatment planning.
Patients are encouraged to consult licensed dental professionals for personalized evaluation and treatment planning.
This information aims to provide a factual overview of dental implants relevant to Canadian readers in 2026. Individual circumstances vary, and it is recommended to seek professional advice for personal dental health needs.




